Google Academy student. Google Academy. What does registering with Google Academy give you?
Search engine Google system created special tool“Google Scholar” for searching scientific and educational literature scholar.google.com, which allows you to search for peer-reviewed articles, dissertations, books and other scientific publications on various sites, from personal sites to large international repositories (storages) and publication databases.
Create this profile first and then use the export button to transfer all the data to other profiles.
Google Scholar not only searches for scientific publications, but also sorts them, assigns them to individual authors, and provides them (the authors) with a service to manage their profile. This service is called “Google Scholar Citations” (GSC for short) or in Russian “Google Scholar Bibliographical Links” or “Google Scholar Author Profile”. You can access this service by opening the Google Scholar page scholar.google.com on the Internet and clicking on the “My Quotes” link (for more details, see the instructions).
Why do you need a Google Scholar Citations profile?
First of all, it is needed by the scientist himself (teacher, researcher). The GSC profile performs several important and convenient functions:
- Systematization of all publishing activity, the broadest of all existing services. Scopus, webscience or RSCI (e-library) collect information about publications only according to a strictly regulated list of publications. Most Russian-language journals and collections of conference proceedings are not included in these databases. Google Scholar indexes all university websites and university repositories, so almost all works are automatically included in the GSC profile.
- Convenient work with the list of publications. You yourself determine the articles of which you are the author, you can edit (clarify) their descriptions, add and delete works.
- When other scientists search Google Scholar, they will be able to see more than just one of your publications. With a GCS profile configured, your last name in the publication description turns into a link, following which you can see the entire list of your works, see the most interesting (most cited), see new works
- Information about scientometric parameters such as Citation Statistics, h-index, i10-index.
- Automatic notification when new links to your publications appear (usually such confirmation comes 1-14 days after publication new job on the Internet, and the publication itself may be in a closed database).
- Automatic notification when new publications appear.
- Export a list of publications in BiBTeX, EndNote, RefMan formats. These formats are understood by researchgate.net and analog systems, personal accounts of scientometric systems. By organizing the list of publications once, you will always have an up-to-date list, and using BiBTeX you can work with it to design new publications in LaTeX format.
- The international ranking Webometrics Ranking World Universities uses the scientometric parameter “Citation Statistics” of the nine most cited university scientists as one of the ranking parameters. You can view this list for BSU by following this link
Any scientific article is based on previously conducted research, so when writing scientific works Often there is a need to access electronic resources - libraries of scientific articles. Google Scholar (Google Academy), Cyberleninka (Kiberleninka) and other systems allow you to search for official scientific publications, without which any scientist is doomed to endlessly “reinvent the wheel.”
Where to find scientific articles
Searching for scientific articles is a process that requires care. There is a lot of unreliable information on the Internet, the use of which can easily distort the results of any study. Electronic resources provide great opportunities to comfortably find the information you need.
Let's figure out where and how to look for scientific articles on the Internet. There are certain sites for searching scientific papers - they are called scientific electronic libraries, catalogs of scientific articles or archives of scientific articles.
Cyberleninka
Cyberleninka is a free Internet portal containing about one million officially published works by scientists, allowing you to search for scientific articles in all areas from psychology to jurisprudence. The user-friendly interface of Cyberleninka allows you to read and search online full-text scientific works. It has an extensive rubricator by areas of activity. Cyberleninka is accessible from any mobile application. Also requires registration. A small drawback of Cyberleninka is the inability to download the text of the article directly from the resource.
Google academy
Google Scholar is a Russified portal for searching officially published articles from scientific journals and various publications. This free service, where you can search and read full-text foreign and Russian articles for free. In addition, dissertations, monographs and other works from various branches of science are available on Google Scholar. Some works are in closed access Google Academy. Access to such publications is possible for a fee. Google has links to citations.
A small drawback of Google Academy is the abundance of pseudoscientific articles.
However, if you have a good command of the subject under study, you will be able to understand the quality of the works posted on the specified service. You can also register as an author and publish your works, as well as track citations. You can also download some articles in PDF format.
eLibrary
This service is an extensive domestic database of articles, numbering more than 37 thousand scientific publications and about 15 million scientific papers. In 2005, the Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI) project was created on the eLybrary platform - a universal citation database similar to Scopus.
The database is available after registration. Registered users can not only search for articles, but also receive a subscription service to electronic publications in various fields of science.
On the portal you can search through the catalog of authors and journals, and use the thematic rubricator.
The library contains articles from Russian and foreign journals, which can be found in open access on-line.
There is a service for creating collections of works on a specific topic, for example, in the field of law, economics, medicine, psychology. Citation links are provided.
Scientific electronic library Scholar.ru
An extensive database of not only literature, but also abstracts and dissertations of scientists. It has a catalog of works by title, author's details, and areas of activity. The advantage of the library is the ability to download the texts of articles from journals. In addition, it is possible to set up a subscription to new arrivals on topics that interest you - law, medicine, economics and other sciences.
Search for scientific articles using ScienceResearch.com
SciencereSearch is a service for worldwide search articles from major scientific journals and publishing houses, as well as archives of scientific literature. The system does not require registration. There are descriptions of abstracts and dissertations.
The search is carried out by the title of the article, the author's data or keywords.
In journals on pedagogy
The SciencereSearch search engine will help you find articles on pedagogy, both in Russian and in most foreign languages world (English, German).
The service contains English-language instructions for use translated into Russian.
The interface is convenient - the data is entered into a single search line, after clicking the search button, a list of articles of interest is displayed, including in psychological areas related to pedagogy.

In psychology journals
The site has an advanced search form; in the rubricator you can find a list of psychological areas of interest. The archive contains many English-language articles from psychology journals.

In defectology journals
To search for articles from defectology journals, you need to go to the “Health and Medicine” section, or enter the terms of interest in the “advanced search” option. The keywords you enter can be found in the text of the article or in the title.
In economics journals
To search for articles from a journal on economics, you also need to use the rubricator.
The strength of the service is automatic translation English-language site into Russian, as well as the ability to download articles. The search engine allows you to find a lot of articles by foreign authors
The search engine provides a range of dates for publications that interest you. When you enter accurate data, the search engine returns a list of more accurate results.
In medical journals
The site contains many foreign articles on medicine, automatically translated into Russian. These articles can be read online or downloaded from the resource. The search engine produces a list of interesting publications by foreign authors.
Where to find scientific articles in English
English articles can be found using the SciencereSearch service described by us.
Google Scholar or Google Scholar - free search system on the full texts of scientific publications of all formats and disciplines. The project was launched in November 2004. To date this system is an indispensable tool for any researcher.
The Google Scholar repository contains information from many peer-reviewed online magazines largest scientific publishing houses in Europe, America and Russia, archives of preprints, publications on the websites of universities, scientific societies and other scientific organizations. The system searches across a variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and judicial opinions from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities and other websites. Google Scholar searches scientific research from all over the world, including articles in Russian.
Google Scholar's advertising slogan - "standing on the shoulders of giants" - is taken from the well-known statement of Isaac Newton, "If I have seen further than others, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants," as a sign of respect to scientists who have made disproportionate contributions to the development of science in the world. over the centuries and laid the basis for modern discoveries and achievements.
In its functionality, Google Scholar is similar to such specialized scientific search engines, electronic archives, tools for searching articles and links, such as Scirus, Science Research Portal, Windows Live Academic, Infotrieve - artical finder, CiteSeerX ResearchIndex, Scientopica and GetCITED. What is also important is that it allows you to work for free, unlike similar sites that provide access to publications after a paid subscription, for example, Scopus and Web of Science.
The following features of Google Scholar can be highlighted:
- searching for scientific literature from any place convenient for you;
- allows you to calculate the publication citation index and find works, citations, authors and articles containing links to those that have already been found;
- the ability to search for the full text of a document both online and through libraries;
- view the latest news and events in any field of research;
- It is possible to create a profile of a public author with links to your publications.
So, let's take a closer look at the available functions of this search engine.
1. Google Scholar Search
The search for a full-text document is carried out not only among publications available online, but also in libraries or paid resources. However, some publishers do not allow the Academy to index their journals.
Search results are ranked by relevance. In accordance with this algorithm, full-text documents are included in the statistics, taking into account the rating of the author or publication that published it and the number of citations from the publication. Thus, the most popular articles are displayed in the first links.
Here you can sort documents by date and citation.

There is also an advanced search that allows you to sort publications by a specific word/phrase, title, author/edition, for a specific period.
2. Quoting and linking
To use this feature, you must create a public Google Scholar profile, complete it, and upload relevant publications. Then, when you search for your name in a search engine, your downloaded publications will appear. Perhaps this will help you make useful contacts with colleagues studying the same issues around the world.
This service will quickly and easily find your articles, regardless of their number and the presence of co-authors.

It is possible to add not only single, but also groups of articles. Citation metrics are calculated and updated automatically as the service discovers new citations of your work on the Internet.
It should be borne in mind that the system does not distinguish between namesakes and, on the contrary, treats identical links received from different/mirror servers as different, in the same way as various options references to the same work. Therefore, a significant investment of time and effort is required to additional processing results of citation determination.
When creating a reference, you will have the opportunity to choose one of the international or Russian standards for the design of bibliographic references.
3. Availability of a webmaster guide
This documentation describes the technology for indexing websites with scientific articles from Google Scholar. It is written for webmasters who would like to have their documents included in the Academy search results.
Detailed Technical information It will also be useful for individual authors who have the opportunity to publish work on their website and add a link to it on the Google Scholar publication page.
By using of this service The global relevance and accessibility of content can be increased by working with scholarly publishers to index peer-reviewed papers, dissertations, preprints, abstracts, and technical reports from all areas of research to make them available on Google and Google Scholar.
4. Metrics or Indicators
This section makes it possible to quickly assess the availability and significance of recent articles in scientific publications, as well as analyze the relevance of the topics for the author.
Here you can view the TOP 100 publications in several languages, ordered by their five-year h-index and h-median. H5 index - Hirsch index for articles published over the last 5 full years. The H5-median is the median of the number of citations of publications that are included in the h5-index.
There is also the opportunity to study publications in specific scientific fields. To do this, you simply need to select the area of research that interests you. Here you can select a subcategory for this area.
As of today, working with categories and subcategories is only available for English publications.

5. Library
Google Scholar uses information about electronic library resources to create item-by-item links to library servers in search results. Using the created database, the user can find the book he needs in the library closest to him.
The mission of Google Scholar is to collect scientific information from around the world in one resource and organize its universality, accessibility and usefulness.
The problem of searching and collecting information is one of the most important problems when writing a scientific publication. Currently, the problem of having too many large quantity information that is not reliable, high quality and relevant.
Thus, the relevance of the problem is determined by the contradiction between the large flows of information circulating in modern world and the inability to quickly and efficiently search for it on the Internet.
When searching the Internet, two components are important - completeness and accuracy. Usually this is all called in one word - relevance, that is, the correspondence of the answer to the question. Important indicators are the coverage and depth of the search engine, crawl speed and relevance of links (the speed at which information is updated in this database), search quality (the closer to the top of the list the document you need is, the better the relevance works).
The scientific search engine Google Scholar is a resource that can solve the problem of finding information and has the ability to quickly and accurately sort it. Due to its expanded functionality, it allows you to find up-to-date, complete and reliable information in any field of research with minimum cost time. According to the creators, Google Scholar allows you to identify the most relevant scientific research from the entire body of work carried out in the world.
The features of this scientific search system can leave a very clear imprint on the processes of intellectual competition and even lead to certain changes in general character scientific results and ideas that survive competition and determine the future of science.
This opportunity brings invaluable benefits for the development of scientific research. Since, on the basis of the information obtained, the author can fully work on the originality and novelty of scientific research.
ONLINE Scientific Journal "Child and Society"
Publisher: International center for the childhood and education (ICCE)
Online ISSN: 2410-2644
Google Scholar is a search system that indexes full texts of scientific publications of all formats and disciplines. Google Scholar includes articles that are published in journals, articles that are stored in repositories or are located on the websites of scientific journals, and the personal pages of scientists.
In order to register in the Google Scholar database, you must first create a Google account. You will be asked to enter some personal information, create email*gmail.com.
After registration we go to home page Google search engine and click the “Login” button in the upper right corner. In a new window, enter the mailbox address and password we specified.

Registration in Google Scholar

You need to go through several registration steps.
Attention (!)- in the “email” field you must enter not your personal mailbox, but the institution where you work.
In order to find out or receive an email from your establishment, you must contact the appropriate information service or department. You can also write a report asking for electronic mailboxes on the official domain of the establishment to one or more employees. In our case, we drew up a report addressed to the first vice-rector of the university from the head of the department. You can get a sample report.

Google Scholar will implement search query based on your last name, first name and patronymic and will offer to indicate or refute the authorship of some articles that have already been indexed. You can skip this step if you are not the author of the found articles.

Choose whether or not to update the list of articles in your profile and move on.
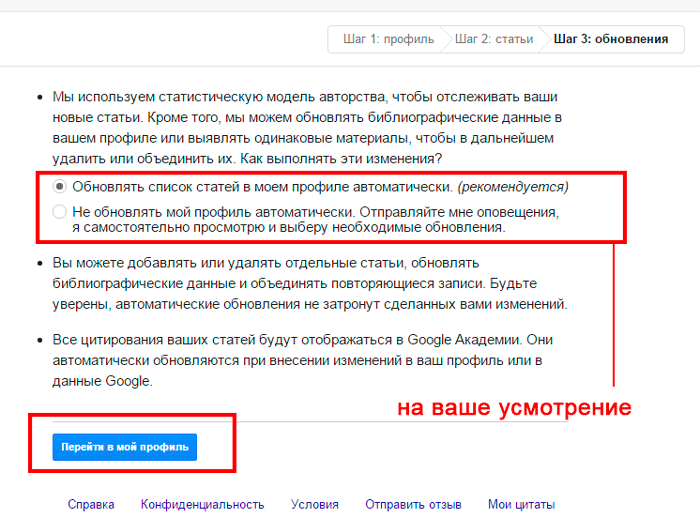
After creating a profile, you need to activate it by clicking on the link that will be sent to the email you specified. Here you can add articles, view citation statistics
How to use Google Scholar?
Google Scholar on the portal Google Scholar) is a freely accessible search engine that provides full-text search for scientific publications of all formats and disciplines. The system has been operating since November 2004, initially in beta version status. The Google Scholar Index includes the majority of peer-reviewed online journals from Europe and America's largest scientific publishers.
It is similar in functionality to the freely available Scirus systems from Elsevier, CiteSeerX And getCITED. It is also similar to tools based on paid subscription, such as Elsevier V Scopus And Thomson ISI's .
Google Academy advertising slogan - "standing on the shoulders of giants"- a tribute to scientists who have contributed to the development of science over the centuries and provided the basis for new discoveries and achievements. Supposedly taken from Newton's quote: "If I have seen further than others, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants."
Google Scholar is Russified, which means scientific articles, theses, books, abstracts, reviews from academic publishing houses and professional societies, online repositories of universities and other popular scientific and educational sites are open to user access.
Google Scholar allows users to search for digital or physical copies of articles, whether online or in libraries. "Scientific" search results are generated using links from full-text journal articles, technical reports, preprints, dissertations, books and other documents, including selected web pages, which are considered "scientific". Since most scientific results Google search- These are direct links to commercial journal articles, most users will only be able to access a short abstract of the article, as well as a small number important information about the article and may have to pay to access the full article. Google Scholar as easy to use as regular Google web search, especially with "Advanced Search", which can automatically narrow search results to specific journals or articles. The most significant keyword search results will be listed in order of the author's ranking, the number of citations that are associated with it and their relationship to other scientific literature, and the publication ranking of the journal in which it appears.
Thanks to its "quoted in" features, Google Scholar provides access to abstracts of articles that cite the article in question. It is this function, in particular, that provides the citation index, previously available only in the Web of Knowledge. This index can be used for webometric ranking of sites. Thanks to its function "Articles on the topic" Google Scholar presents a list of closely related articles, ranked primarily by how similar the articles are to the original result, but also by the significance of each article.
What do you get from registering with Google Academy?
If before registration Google Academy could only be used as a means of searching for articles by other authors, then after registration, this site will help you track the dynamics of citations of your own works. You can not only see the total number of citations, but also find out who and when referred to your work, build a citation chart and determine the currently popular scientometric indicators.
Also, Academy users can make their profile accessible, and then the link to your profile will be visible to users viewing your work. Perhaps this will help you make useful contacts with colleagues studying the same issues around the world.
Google Scholar can make your work more visible to the scientific community around the world. Google Scholar uses information about electronic library resources to create item-by-item links to library servers in search results. With the help of the database database that is created, the user can find the desired book in the library nearest to him.
Watch online: How to use Google Scholar
Limitations of indexing and criticism of the ranking algorithm
 While most academic databases and search engines allow users to select one of the factors (such as relevance, number of citations, or publication date) to rank results, Google Scholar ranks results using a combined ranking algorithm. Google Scholar places particular weight on the number of citations and words included in the title of a document. As a result, the first search results often contain highly cited articles.
While most academic databases and search engines allow users to select one of the factors (such as relevance, number of citations, or publication date) to rank results, Google Scholar ranks results using a combined ranking algorithm. Google Scholar places particular weight on the number of citations and words included in the title of a document. As a result, the first search results often contain highly cited articles.
A significant problem with Google Scholar is the lack of data on its coverage. Some publishers do not allow her to index their journals. Magazines Elsevier were not included in the index until mid-2007, when Elsevier made most of its content on ScienceDirect available for Google Scholar on Google Web Search. Google Scholar does not publish crawl lists of scientific journals. Its update frequency is also unknown. However, it provides easy access to published articles without the hassle of some of the most expensive commercial databases.
In addition, this academic search engine is currently filled with pseudoscientific articles, making it a potentially dangerous database for those doing serious research, from students to scientists. The problem is that Google Scholar strives to index as fully as possible articles appearing in scientific journals. However, many unscrupulous publishers use indexing mechanisms Google Scholar and includes in its index numerous pseudoscientific or insufficiently high-quality publications that would not pass the peer review process in scientific journals.

